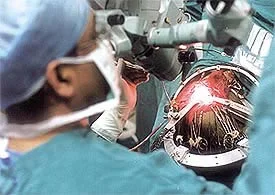
Minimally Invasive Neurosurgery (MIS)
Minimally Invasive Neurosurgical (MIS) techniques offer neurosurgeons a great improvement in working conditions to achieve effective neurosurgery and an improved outcome for patient conditions including:
Brain tumours: Brain Tumours may be Primary or Secondary (metastasized brain tumours)
Pituitary brain tumours: Brain tumours originating from the pituitary gland
Intracranial (brain) aneurysms: Bulge or ballooning of a brain blood vessel
Trigeminal Neuralgia: Trigeminal nerve disorder causing sudden, intense facial pain
Brain lesions: Abnormal brain tissue
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery (MISS): Keyhole or minimal access spine surgery
Minimally Invasive Neurosurgery (MIS) is not just the sole use of a microscope during a conventional neurosurgical exploration. It is an entirely new surgical discipline and concept requiring the use of a mobile counter-balanced operating microscope, and necessitating mastery of indirect eye-hand interaction which can only be acquired in a specially equipped laboratory.
Minimally Invasive Surgery (MIS) has two main components:
1. Special equipment:
Counter-balanced mobile operating microscope equipped with T.V. camera and monitors to enhance and promote team work in the operating room between surgeon, neuroanesthesiologist, nurses, and technicians.
Bipolar coagulators and bipolar forceps of different lengths and tip size. Also “Isocool” (J&J product) bipolar tips that need minimal cleaning due to patented internal thermodynamic countercurrent cooling mechanism.
Pressure regulated suction apparatus and suction tubes in different lengths and diameters.
Bayonet-shaped surgical instruments in different lengths and tip sizes and malleable microinstruments.
Microsutures and special needle holders.
Self-retaining "protective" brain retractors.
Hydraulic chair and adjustable arm rest for the surgeon.
Magnified Loupes (glasses for general Neurosurgery, peripheral nerve surgery and spinal surgery outside the dura (spinal cord and root covering). Also used with a headlight for optimal lighting.
2. Special surgical techniques requiring laboratory training:
Enhanced eye-hand interaction working under conditions of indirect vision with the operating microscope.
Delicate manipulation with microinstruments during dissection, clipping, coagulating, neurovascular repair, and grafting.
Tactics to operating within a key-hole approach performing the procedures as mentioned above; but, under more difficult conditions, for example plastic boxes of different heights (5-12 cm) and with narrow openings cm diameter) simulate deep narrow approaches within and around the brain. RACS workshops and accredited Microneurosurgical courses. Also Da Vinci robotic surgical techniques used in Urology.
Delicate and controlled manipulations within the confines of a small gap and using a self-retaining protective brain retractor.
Training the use and applications of the bipolar coagulator and microsuction equipment.
Training to develop expertise and comfort using high-speed surgical drills. i.e. Midas Rex (Medtronic) drill workshops accredited world-wide.